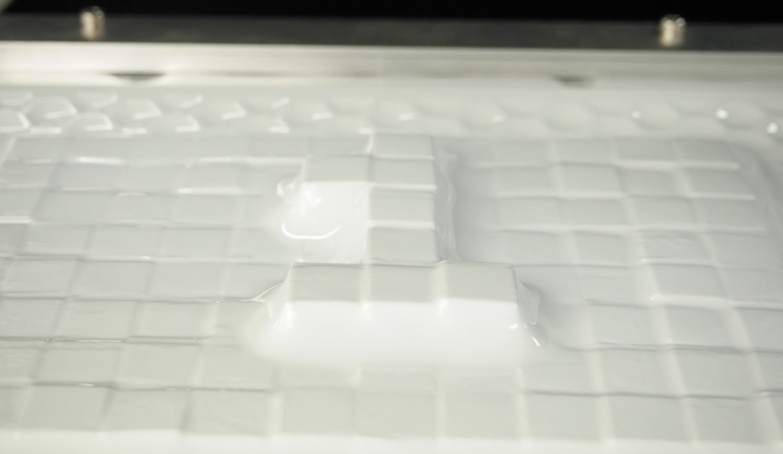
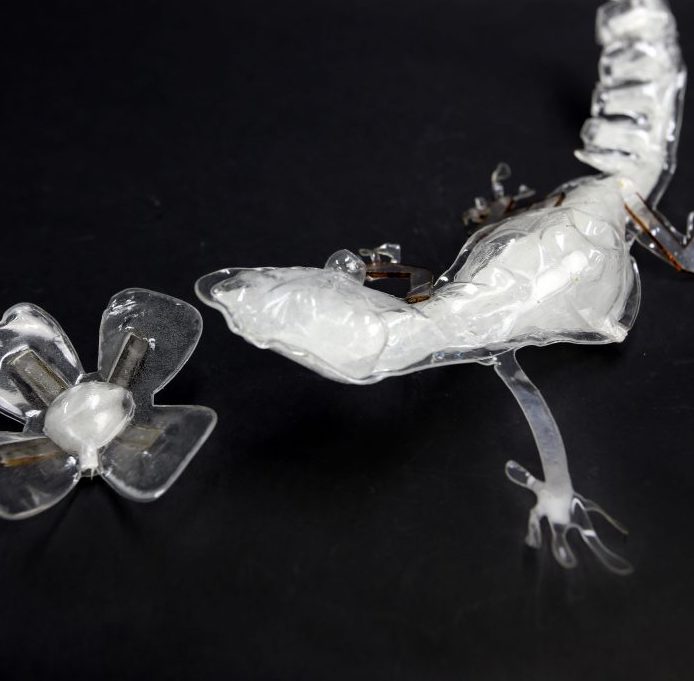
Blowfabは、レーザーカッターとブロー成形を組み合わせることで、高速に再利用可能な2.5Dオブジェクトを作成できるプロトタイピング手法である。マスキングテープ、PETからなる多層構造のプラスチック板をレーザー加工することで、粘着箇所と空洞箇所を作成する。その後、2枚を重ね、ヒータを用いて温めることで板が軟化し、粘着箇所が自然に熱融着する。軟化時に空気を注入することで、硬質なプロトタイプを作ることができる。さらにカットパターンを工夫したり、耐熱樹脂を組み合わせることで、任意の角度に曲げたり、耐熱フィルムを用いることで表面に凹凸加工を施すことができる。
BlowFab is a prototyping method used to create a 2.5-dimensional prototype in a short time by combining laser cutting and blow molding techniques. The user creates adhesive areas and inflatable areas by engraving and cutting multilayered plastic sheets using a laser cutter. These adhesive areas are fused automatically by overlapping two crafted sheets and softening them with a heater. The user can then create hard prototypes by injecting air into the sheets. Objects can be bent in any direction by cutting incisions or engraving a resistant resin. The user can create uneven textures by engraving a pattern with a heat-resistant film.
UIST2017 [honorable mention]
Junichi Yamaoka, Ryuma Niiyama, and Yasuaki Kakehi. 2017. BlowFab: Rapid Prototyping for Rigid and Reusable Objects using Inflation of Laser-cut Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST ’17). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 461-469.
https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=3126624